Understanding Angioedema and Urticaria: Diagnosis and Care
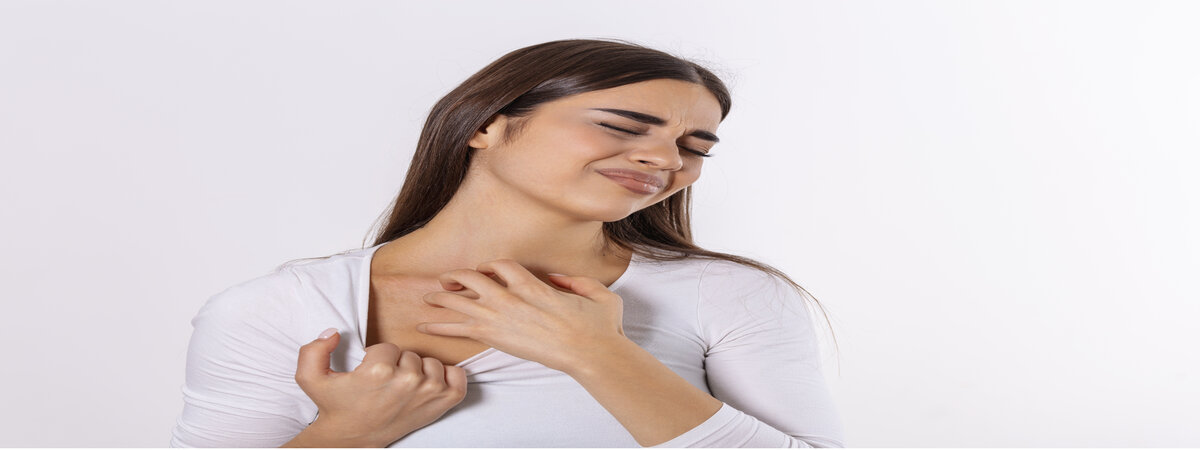
Ever had those red, itchy patches pop up out of nowhere? Or maybe you’ve noticed swelling in your face or throat that made you pause? Those could be hives (urticaria) or angioedema, two skin issues that can feel like a mystery. As a dermatologist, I’ve helped tons of folks figure out what’s going on with their skin, and I’m here to break it down for you—clear, simple, and straight from the heart.
What’s Happening with Hives and Angioedema?
Hives are those red, raised spots that itch like nobody’s business. They can show up on your arms, back, or even your face, and they love to shift around. Angioedema is a bit different—it’s swelling that happens deeper in your skin, often around your lips, eyes, or throat. It can feel alarming, especially if it messes with your breathing or swallowing.
Both are usually your body’s way of saying, “Hey, something’s setting me off!” That “something” could be an allergy (like to food, pollen, or meds), stress, or even a bug your immune system’s fighting.
Why Do These Two Show Up Together?
Hives and angioedema are like best friends—they often hang out together. Why? They’re both sparked by your immune system reacting to a trigger. When it senses something it doesn’t like, it pumps out chemicals like histamine, which can cause those itchy welts or deeper swelling. Sometimes you’ll get both at once, or one after the other.
This overlap is why we dig deep to understand what’s going on. It’s not just about slapping on a cream—it’s about getting the full picture so we can stop these flare-ups for good.
Are They a Big Deal?
Hives can drive you up the wall with the itching, but they usually fade in a day or two. Angioedema, though, can be more serious. If swelling hits your throat or tongue, it might make breathing tough—that’s when you need help ASAP. If you ever feel like you can’t breathe right, don’t wait; head to the ER.
But here’s the reassuring part: most cases are totally manageable. We’ve helped patients like Mark, who had angioedema from a new medication, find the right plan to keep it under control. You don’t have to live with the worry.
How Do We Figure Out What’s Causing It?
Getting to the bottom of hives or angioedema is like being a detective. Here’s what we do:
-
Chat about your life: We’ll talk about when your symptoms started, what you’ve been eating, any new meds, or even if you’ve been super stressed.
-
Run some tests: Blood tests can show if your immune system’s acting up or if there’s a specific allergy at play.
-
Allergy checks: We might do skin tests to see if something like pet dander or pollen is the culprit.
Everyone’s different, so we make sure our approach fits you. No one-size-fits-all here.
What Can You Do About It?
Good news—there are solid ways to tackle hives and angioedema. Here’s what works:
-
Antihistamines: These are your go-to for calming the itch and swelling by blocking histamine.
-
Steroids: For bigger flare-ups, a short burst of steroids can settle things down.
-
Emergency kits: If angioedema could affect your breathing, we might suggest carrying an adrenaline injector (like an EpiPen).
-
Smart habits: Steering clear of triggers, chilling out with stress-relief tricks, and drinking plenty of water can help a ton.
If your hives stick around for weeks (what we call chronic hives), we’ve got advanced options and can team up with allergy specialists to get you relief.
Easy Tips to Feel Better Fast
-
Cool it off: A cold, damp towel can soothe the itch in minutes.
-
Don’t scratch: It’s tempting, but it can make things worse or cause infections.
-
Play detective: Jot down when symptoms hit to spot what’s setting them off.
-
Be ready: If angioedema’s a repeat issue, keep your meds close by.
Why Trust Us with Your Skin?
At our dermatology clinic in London, we’re all about you. Our board-certified dermatologists know allergies and skin conditions inside out, and we’re here to create a plan that fits your life. Patients tell us they love how we listen—really listen—and explain things in a way that makes sense.
Whether you’re fed up with itchy hives that keep coming back or worried about swelling that catches you off guard, we’ve got your back. We blend the latest tech with a warm, human touch so you walk out feeling understood and hopeful.
Ready to Get Answers?
If you’re wondering, “Why does my skin keep doing this?” let’s find out together. Schedule a chat with our team today, and we’ll dig into what’s causing your symptoms and how to fix it. No guesswork, no fluff—just a plan that works for you.
FAQ
Can angioedema affect the eyes?
Angioedema primarily affects deeper skin layers, but in some cases, it can lead to swelling around the eyes, which may impair vision or cause discomfort.
Is there a cure for urticaria and angioedema?
While there may not be a permanent cure, various treatment options can effectively manage symptoms and provide relief. Consultation with a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the most suitable approach for individual cases.
What are common triggers for urticaria and angioedema?
Allergies to substances like certain foods, medications, insect stings, and environmental factors are common triggers. Stress, infections, and underlying medical conditions can also contribute.
How are allergies related to urticaria and angioedema?
Allergic reactions can prompt the release of histamines, which can lead to urticaria and angioedema in some individuals. Identifying specific allergens can aid in managing these conditions.
Are there preventive measures for these skin conditions?
Avoiding known allergens and triggers is a key preventive measure. Additionally, stress management and proper medication adherence can help reduce the frequency and severity of episodes.
What is the role of antihistamines in treating urticaria and angioedema?
Antihistamines are often prescribed to manage symptoms, as they can counteract the effects of histamine release, which is a common factor in these conditions.
When should I seek emergency medical attention for angioedema?
If angioedema affects the airway, causing difficulty breathing or swallowing, or if it occurs alongside severe allergic reactions, seek immediate medical help, as it can be life-threatening.
Is it possible for urticaria or angioedema to be chronic?
Yes, chronic urticaria and angioedema can persist for months or even years. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for long-term management.


